22年1月算法笔记
Typora加超链接实现页内跳转的三种方法_AZZJXHDSGIRL的博客-CSDN博客_typora超链接怎么用
RE&&WA错误
1.数组开太小
2.数组开太大
3.出现了除以0
4.算法不够优化

排列组合
有顺序用排列

无顺序用组合

Scanner
String num = sc.nextLine();
String[] arr = num.split(" ");
以空格为分割,存到数组中
特殊符号
0为false 1为true
|=:两个二进制对应位都为0时,结果等于0,否则结果等于1;
&=:两个二进制的对应位都为1时,结果为1,否则结果等于0;
^=:两个二进制的对应位相同,结果为0,否则结果为1。
printf
Java中printf()方法的用法 - 百度文库 (baidu.com)
printf(“%3d\t”) 输出一个整数定长为3字符的整数,按右对齐输出,在输出一个tab位
大小写字母转换
大写转小写 a.toLowerCase();
小写转大写 a.toUpperCase();

数据类型的转化
integer.toString和String.valueOf的区别
通过源码,可以看到区别在于 当转换的obj==null的时候
Integer.toString() 会报空指针异常(NullPointerException)
String.valueOf()则会返回 “null” 字符串(return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();)
Float.toString(m); //转化为字符串
Float.parseFloat(b); //转化为基本数据类型
(float)a; //基本数据间的转化
Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(arr[i]))) //char转化为int
char c=63; //int类型转化为char(自动转化) char c=(char)63
char类型转化为int类型
char ch = '9';
if (Character.isDigit(ch)){ // 判断是否是数字
int num = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(ch));
System.out.println(num);
}
char ch = '9';
if (Character.isDigit(ch)){ // 判断是否是数字
int num = (int)ch - (int)('0');
System.out.println(num);
}
char转化为Strng
public static void main(String[] args) {
// char to string
char c = 'a';
String str = String.valueOf(c);
// using Character class
str = Character.toString(c);
// another way
str = new Character(c).toString();
// string concatenation - worst performance
str = "" + c;
// char array to string
char[] ca = { 'a', 'b', 'c' };
str = String.valueOf(ca);
// recommended way
str = new String(ca);
}
String与int互相转换
Int----->String(4种方法)
int num=100;
//1
String s1=""+num;
//2
String s2 =String.valueOf(num); (Double.valueOf 转化为Double类型)
//3
Integer i =new Integer(num);
String s3 =i.toString();
//4
String s4 =Integer.toString(i);
String---->Int (2种)
String s="100";
//1
Integer ii =new Integer(s);
int x=ii.intValue();
//2
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
String--->long
long l = Long.parseLong([String],[int radix]);
long l = Long.valueOf(“123”).longValue();
区别:
Long.ValueOf(“String”)返回Long包装类型
Long.parseLong(“String”)返回long基本数据类型
设置小数点位数 && 有效数字
方法一:String.foramt("%.f",d)
double d=6.235;
String s=String.format("%.2f", d);
System.out.println(s);
//输出:6.24,说明已经进行四舍五入了。
方法二:使用DecimalFormat类
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
...
double d=6.345;
DecimalFormant df=new DecimalFormant("0.00");
System.out.println(df.formant(d));
//输出:6.34 进行四舍五入
...
方法三:
double f = 12345.67890;
BigDecimal bg = new BigDecimal(f);
double f1 = bg.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
System.out.println(f1);
方法四:
double f = 12345.67890;
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);
System.out.println(nf.format(f));//12,345.68
空格不能用"\t"

浮点型强制转型(int)等于向下取整
格式化数字“001”
DecimalFormat df1 = new DecimalFormat("000");//如果小于100就用他
String emNum = df1.format(1);//结果就是001
科学计数法
//科学计数法数字转普通数字
double num1 = 50123.12E25;
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(num1);
System.out.println(bd1.toPlainString());
//普通数字转科学计数法
double num2 = 50123.12;
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal(num2);
System.out.println(bd2.toPlainString()); //法一
System.out.println(String.format("%.6E",num2)); //法二
算数平方根
java.lang.Math.sqrt(double a)
向上取整用Math.ceil(double a) ----->ceil天花板
向下取整用Math.floor(double a) ----->floor地板
数组集合排序
基本数据类型的默认值:
①byte short int long 这四种基本数据类型数组默认值为0
②float double 这两种数组默认值是0.0
③char这种类型数组默认值为空格
④boolean类型数组默认值为false
sort
在java.util.Collections类中有个sort()方法,主要是用来给数组排序,排序的规则可以自己重写。
(一)给数组{2,3,1,5}按自小到大排序
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(1);
list.add(5);
Collections.sort(list);
for(Integer i:list)
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
输出结果为:
1 2 3 5
(二)把数组从大到小排序
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(1);
list.add(5);
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if(o1>o2)
return -1;
else if(o1
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
});
for(Integer i:list)
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
结果为:
5 3 2 1
Sort对数组
升序
使用 java.util.Arrays 类中的 sort() 方法对数组进行升序分为以下两步:
- 导入 java.util.Arrays 包。
- 使用 Arrays.sort(数组名) 语法对数组进行排序,排序规则是从小到大,即升序。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义含有5个元素的数组
double[] scores = new double[] { 78, 45, 85, 97, 87 };
System.out.println("排序前数组内容如下:");
// 对scores数组进行循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
System.out.print(scores[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println("\n排序后的数组内容如下:");
// 对数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(scores);
// 遍历排序后的数组
for (int j = 0; j < scores.length; j++) {
System.out.print(scores[j] + "\t");
}
}
排序后的数组内容如下:
45.0 78.0 85.0 87.0 97.0
降序
1)利用 Collections.reverseOrder() 方法(Collections 是一个包装类。《Java Collections类》一节详细了解):
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = { 9, 8, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 6, 5 }; // 数组类型为Integer
Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int arr : a) {
System.out.print(arr + " ");
}
}
输出结果如下:
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
集合
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(1);
list.add(5);
Collections.sort(list);//从小到大
Collections.sort(list,Collections.reverseOrder());//从大到小
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.print(o+" ");
}
}
集合反转
Collections.reverse(arr);
数组标法记某个数出现的次数
import java.util.Scanner;
//梦中的婚礼
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int M = input.nextInt(), N = input.nextInt();
int[] num = new int[10];
for (int i = M; i <= N; i++)
for (int temp = i; temp != 0; temp /= 10)
num[temp%10]++;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
}
}
}
public class p1554梦中的统计 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner rd =new Scanner(System.in);
int a = rd.nextInt(); //小的
int b = rd.nextInt(); //大的
int t = b - a;
int arr [] = new int [10]; //存0~9的数组
for(int i = a; i<=b;i++) {
int c = i;
while(c != 0) {
arr [c%10]++;
c/=10;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P2911G {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int [] a = new int[3];
int [] b = new int [20000000];//计数数组
int max = - Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
a[i] = cin.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);
for(int x = 1; x <= a[0]; x++) {
for(int y = 1; y <= a[1]; y++) {
for(int z = 1; z <= a[2]; z++)
b[x+y+z]++;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
if(b[i] > max)
max = b[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
if (b[i]==max) {
System.out.println(i);//输出最大那个数字的数组下标
break;
}
}
}
}
把ArrayList转换成普通数组
int len = arr.size(); //获取集合长度
Integer[] newArr = new Integer[len]; //创建数组
arr.toArray(newArr); //转为数组
大数字精度问题
BigInteger、BigDecimal
BigInteger
package ustc.lichunchun.bigdataapi;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class BigIntegerDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bi1 = new BigInteger("123456789") ; // 声明BigInteger对象
BigInteger bi2 = new BigInteger("987654321") ; // 声明BigInteger对象
System.out.println("加法操作:" + bi2.add(bi1)) ; // 加法操作
System.out.println("减法操作:" + bi2.subtract(bi1)) ; // 减法操作
System.out.println("乘法操作:" + bi2.multiply(bi1)) ; // 乘法操作
System.out.println("除法操作:" + bi2.divide(bi1)) ; // 除法操作
System.out.println("最大数:" + bi2.max(bi1)) ; // 求出最大数
System.out.println("最小数:" + bi2.min(bi1)) ; // 求出最小数
BigInteger result[] = bi2.divideAndRemainder(bi1) ; // 求出余数的除法操作
System.out.println("商是:" + result[0] +
";余数是:" + result[1]) ;
}
}
BigDecimal
package ustc.lichunchun.bigdataapi;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimalDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("加法运算:" + MyMath.round(MyMath.add(10.345,3.333),1)) ;
System.out.println("减法运算:" + MyMath.round(MyMath.sub(10.345,3.333),3)) ;
System.out.println("乘法运算:" + MyMath.round(MyMath.mul(10.345,3.333),4)) ;
System.out.println("除法运算:" + MyMath.div(10.345,3.333,3)) ;
}
}
class MyMath{
public static double add(double d1,double d2){ // 进行加法计算
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(d1) ;
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(d2) ;
return b1.add(b2).doubleValue() ;
}
public static double sub(double d1,double d2){ // 进行减法计算
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(d1) ;
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(d2) ;
return b1.subtract(b2).doubleValue() ;
}
public static double mul(double d1,double d2){ // 进行乘法计算
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(d1) ;
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(d2) ;
return b1.multiply(b2).doubleValue() ;
}
public static double div(double d1,double d2,int len){ // 进行除法计算
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(d1) ;
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(d2) ;
return b1.divide(b2,len,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue() ;
}
public static double round(double d,int len){ // 进行四舍五入
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(d) ;
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(1) ; // 技巧
return b1.divide(b2,len,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue() ;
}
};
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1009阶层之和高精度 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
BigInteger sum =new BigInteger("0");
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
sum.add(mul(i));
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
//求单个数字的阶层
public static BigInteger mul(int n) {
BigInteger m=new BigInteger("1");
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
m=m.multiply(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(i)));
}
return m;
}
}

字符串
删除字符串
//要切割的字符串
String s = "123.jpg,113.jpg,121.jpg,122.jpg,131.jpg";
String sub = "";
System.out.println("编译前:"+s);
//调用方法
sub = s.replaceAll( ",113.jpg|113.jpg,","");//.replaceAll( ",122.jpg|122.jpg,","");
System.out.println("编译后:"+sub);
求最大公约数
public static int common(int m,int n) {
int r=1;
for (int i=2;i<=m && i<=n;i++) {
if (m%i ==0 && n%i==0) {
r=i;
}
}
return r;
}
检测代码运行时间
一、以毫秒为单位。
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
doSomething(); //测试的代码段
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间
求最小值
int a[] = {10, 5, 8};
int min = Arrays.stream(a).min().getAsInt();
//或 Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(a[0]);
质数判断&&数字反转
//数字反转
public static boolean reverse(long a) {
/*100分*/
long x = a;
// String y = "";//字符串会延长时间
long y=0;
while (x != 0) {
y = y*10 + x % 10;
x = x / 10;
}
if (y == a) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
/*88分*/
// long d=a;
// String mid ="";
// while (a!=0) {
// long b=a%10;
// a=a/10;
// mid+=b;
// }
// if ((Long.parseLong(mid)==d)){
// return true;
// }else {
// return false;
// }
}
//质数判断
public static boolean judge3(long n) {
if (n == 1 || n == 2 || n == 3) {
return true;
} else {
for (int i = 2; i <= (Math.sqrt(n)); i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
//质数判断
private static boolean isPrime(int src) {
double sqrt = Math.sqrt(src);
if (src < 2) {
return false;
}
if (src == 2 || src == 3) {
return true;
}
if (src % 2 == 0) {// 先判断是否为偶数,若偶数就直接结束程序
return false;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= sqrt; i+=2) {//不带“=” 41分
if (src % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//质数判读
public static boolean judge(long i) {
if (i<2) {
return false;
}
for (int j=2;j<i;j++) {
if (i%j==0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
数字反转2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P5705数字反转 {
public static void main(String []args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
float m= scanner.nextFloat();
String a = Float.toString(m);
String b = new StringBuffer(a).reverse().toString();//
float c = Float.parseFloat(b);
if (m>=100&&m<1000) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}
质数判断
private static boolean isPrime(int src) {
double sqrt = Math.sqrt(src);
if (src < 2) {
return false;
}
if (src == 2 || src == 3) {
return true;
}
if (src % 2 == 0) {// 先判断是否为偶数,若偶数就直接结束程序
return false;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= sqrt; i+=2) {
if (src % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
数字反转
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a= scanner.nextInt();
int sum =0;
while (a!=0) {
sum = sum*10 + a%10;
a=a/10;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
Math类的常用方法
Math.sqrt() //计算平方根
Math.cbrt() //计算立方根
Math.hypot(x,y) //计算 (x的平方+y的平方)的平方根
Math.pow(a,b) //计算a的b次方
Math.abs(a) //求绝对值
Math.ceil() //向上取整
Math.floor() //向下取整
HashSet不重复集合
Set<String> S = new HashSet<String>(); //构造字符串集合S
//主要方法
S.add() //增加元素
S.clear() //从此 set 中移除所有元素
S.remove() //如果指定元素存在于此 set 中,则将其移除
S.size() //返回此 set 中的元素的数量(set 的容量)
Map遍历方法
Map<Integer,Integer> list = new TreeMap<>();
list.put(1,3);
list.put(3,7);
list.put(4,2);
list.put(2,5);
int a = list.get(4);
a++;
list.put(4,a);
System.out.println(a);
//方法一单独遍历
for (Integer key: list.keySet()) {
// System.out.print(key+" ");
}
for (Integer values:list.values()) {
// values++;
// System.out.print("\n"+values+" ");
}
//方法二 一起遍历
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> arr :list.entrySet()) {
int m=arr.getKey();
int n=arr.getValue();
System.out.println(m+","+n);
}
Map综合利用求集合出现最多次数
{//P2911
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int s1=scanner.nextInt(),s2=scanner.nextInt(),s3=scanner.nextInt();
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
int sum=0;
for (int i =1;i<=s1;i++) {
for (int j =1;j<=s2;j++) {
for (int k =1;k<=s3;k++) {
sum = i+j+k;
arr.add(sum);
}
}
}
Collections.sort(arr);
Map <Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer integer : arr) {
// System.out.println(integer);
if (!map.containsKey(integer)) {
map.put(integer,1);
}else {
int a = map.get(integer);
a++;
map.put(integer,a);
}
}
int max=0;
for (Integer a:map.values()) {
if (a>max) {
max=a;
}
}
// System.out.println(max);
int key=0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> map1 :map.entrySet()){
// System.out.println(map1.getKey()+","+map1.getValue());
if (map1.getValue()==max) {
key=map1.getKey();
break;
}
}
System.out.println(key);
}
截取字符串&&替换字符串
substring() 方法截取v字符串
字符串.substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
//beginIndex 起始索引(包括), 索引从 0 开始。endIndex 结束索引(不包括)。
替换字符串中的片段
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("abcdefghijklmn");
str=str.replace(3, 6, "这里被换了"); //变成了 abc这里被换了ghijklmn
替换字符串中的一个字符
String str = new String("abcdefghijklmn");
str=str.replace("a", "这里被换了"); //变成了 这里被换了bcdefghijklmn
拆分字符串split()
split() 方法根据匹配给定的正则表达式来
针对string类型的split()函数。它主要是切割字符串,结果返回由字符串元素组成的一个列表
-
当****没有参数*的情况下,函数默认会以*空格,回车符,空格符****等作为分割条件。
-
有参数函数会****以参数为分割条件**,把字符串进行分割,得到的每个分割段作为列表的元素返回**。
-
两个参数,****第二个参数的意思是你想分多少次****
-
a="My,name,is,zhangkang,and,I,am,a,student" b1=a.split(",",1) b2=a.split(",",2) b8=a.split(",",8) b9=a.split(",",9) //大于最大值不会报错 print(b1) print(b2) print(b8) print(b9) 输出: ['My', 'name,is,zhangkang,and,I,am,a,student'] ['My', 'name', 'is,zhangkang,and,I,am,a,student'] ['My', 'name', 'is', 'zhangkang', 'and', 'I', 'am', 'a', 'student'] ['My', 'name', 'is', 'zhangkang', 'and', 'I', 'am', 'a', 'student']
String str = new String("Welcome-to-here");
for (String retval: str.split("-"))
System.out.println(retval);
/*
输出结果为:
Welcome
to
here
*/
字符串反转&&字符串拆分
charAt(i) 函数 是获取字符串中i位置的字符
String a= "123ad" ;
//方法一 利用StringBuffer的reverse
String a1=new StringBuffer(a).reverse().toString();
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println("1.=====================");
//方法二 利用String的toCharArray方法先将字符串转化为char类型的数组,然后将各个字符进行从新拼接
char [] chars = a.toCharArray();
String a2="";
for (int i=chars.length-1;i>=0;i--) {
a2 +=chars[i];
}
System.out.println(a2);
System.out.println("2.=====================");
//方法三 利用String的CharAt方法取出字符串中的各个字符
String a3 = "";
for (int i=0;i<a.length();i++){
a3=a.charAt(i) + a3;
}
System.out.println(a3);
System.out.println("3.===================");
public class RunoobTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String Str = new String("This is text");
System.out.print("返回值 :" );
System.out.println(Str.substring(4) );
System.out.print("返回值 :" );
System.out.println(Str.substring(4, 10) );
}
}
返回值 : is text
返回值 : is te
判断字符串开头结尾

indexOf函数两种用法
1、 indexOf(String str): 返回指定字符str在字符串中(方法调用者)第一次出现处的起始索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。
2、indexOf(String str, int index): 返回从 index 位置开始查找指定字符str在字符串中第一次出现处的起始索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。
计算某字符串中特定字符串出现次数的几种算法
利用indexOf()方法
/**
* str.indexOf(findstr,index) 从index开始 有这个字符串,返回这个字符串第一次出现的下标。没有则返回-1
*/
public class 标记某个字符出现的次数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "jhdvjsdjava;osdfpojavalsdjfisjavlsdihgjavalsdihfsjava";
String findstr = "java";
int count = countstr5(str,findstr);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static int countstr5(String str,String findstr){
int count = 0;
int index = 0;
//如果!=-1,则说明找到了findstr首次出现的索引
while((index = str.indexOf(findstr,index)) != -1){
System.out.println(str.indexOf(findstr,index));
System.out.println(index);
index += findstr.length();//去除之前检测过的字符串
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
-
出现次数 = (原字符串长度 - 替换后字符串长度) / 目标子串长度
public class 标记某个字符串出现的次数_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "jhdvjsdjava;osdfpojavalsdjfisjavlsdihgjavalsdihfsjava";
String findstr = "java";
int count =countstr1(str,findstr);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static int countstr1(String str,String findstr){
int count = 0;
count = (str.length() - str.replace(findstr,"").length())/findstr.length();
return count;
}
}
indexOf()方法 搭配 subString()方法
select substring(‘abdcsef’,1,3)
结果:‘abd’
- 利用substring方法截取(最近子串结束的位置 ,字符串末尾)
在指定位置拼接和插入字符串
Java——在指定位置拼接和插入字符串_命中的缘分的博客-CSDN博客_java string 插入
末尾插入
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder("1234ac");
stringBuilder.append("123");
位置插入
StringBuffer stringBuilder1=new StringBuffer("20180918");
stringBuilder1.insert(6,"-");
stringBuilder1.insert(4,"-");
字符后插入
StringBuilder stringBuilder2=new StringBuilder("1234abcdabc12");
int index=stringBuilder2.indexOf("abc");
stringBuilder2.insert(index,"131");
String StringBuffer StringBuilder 转换
String:不可变的字符序列
StringBuffer:可变的字符序列,线程安全、效率低
StringBuilder: 可变的字符序列,jdk5.0 新增 效率高
-
String开始创建的是一个长度为0的字符数组
StringBuffer StringBuilder 底层创建了一个长度是16的字符数组。
初始化有值时 创建一个长度为字符长度+16的字符数组。
扩容为原来的两倍+2 同时将数组中的元素复制到新的数组中
指定大小,防止持续扩容
StringBuffer(int capacity)
StringBuilder(int capacity) -
对比String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder三者的执行效率
从高到低排列:StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String -
String与StringBuffer、StringBuilder之间的转换:
String -->StringBuffer、StringBuilder:调用StringBuffer、StringBuilder构造器 -
StringBuffer、StringBuilder -->String:
①调用String构造器;
②StringBuffer、StringBuilder的toString()
==和equals在比较字符串时候的区别 - 菜鸟~风 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
简单说==指向同一对象(内存地址),equals用于比较两个对象是否相等
正则
-
find()方法是部分匹配,是查找输入串中与模式匹配的子串,如果该匹配的串有组还可以使用group()函数。
-
matches()是全部匹配,是将整个输入串与模式匹配,如果要验证一个输入的数据是否为数字类型或其他类型,一般要用matches()。
-
1.matches:整个匹配,只有整个字符序列完全匹配成功,才返回True,否则返回False。但如果前部分匹配成功,将移动下次匹配的位置。
2.lookingAt:部分匹配,总是从第一个字符进行匹配,匹配成功了不再继续匹配,匹配失败了,也不继续匹配。从第一个匹配,匹配一次,只要第一个失败就返回false 不在匹配
3.find:部分匹配,从当前位置开始匹配,找到一个匹配的子串,将移动下次匹配的位置。
4.reset:给当前的Matcher对象配上个新的目标,目标是就该方法的参数;如果不给参数,reset会把Matcher设到当前字符串的开始处。
正则表达式中的 .? 或 .+ 或.*
-
src=".*"
匹配结果是:src="test.jpg" width="60px" height="80px"
意思是从="往后匹配,直到最后一个"匹配结束 -
懒惰模式正则:
src=".*?"
结果:src="test.jpg"
因为匹配到第一个"就结束了一次匹配。不会继续向后匹配。因为他懒惰嘛。 -
.表示除\n之外的任意字符
*表示匹配0-无穷
+表示匹配1-无穷
####find() + start() + end()
find() 方法用于在文本中查找出现的正则表达式,文本是创建Matcher时,通过 Pattern.matcher(text) 方法传入的。如果在文本中多次匹配,find() 方法返回第一个,之后每次调用 find() 都会返回下一个。
start() 和 end() 返回每次匹配的字串在整个文本中的开始和结束位置。实际上, end() 返回的是字符串末尾的后一位,这样,可以在把 start() 和 end() 的返回值直接用在String.substring() 里。
String text =
"This is the text which is to be searched " +
"for occurrences of the word 'is'.";
String patternString = "is";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(text);
int count = 0;
while(matcher.find()) {
count++;
System.out.println("found: " + count + " : " + matcher.start() + " - " + matcher.end());
System.out.println(text.substring(matcher.start(), matcher.end()));
}
Pattern pat = Pattern.compile(regEx,Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
表示正则regEx不区分大小写
HashSet不重复集合
Set<String> S = new HashSet<String>(); //构造字符串集合S
//主要方法
S.add() //增加元素
S.clear() //从此 set 中移除所有元素
S.remove() //如果指定元素存在于此 set 中,则将其移除
S.size() //返回此 set 中的元素的数量(set 的容量)
标题算法学习前的初步了解
注意:从此处到以下(到2.冒泡排序查找)是之前总结,大部分是从知乎和博文上复制来的。有些有附上博文链接,有些没附上,此博文仅代表是本人的笔记记录。
java知识
(2条消息) java算法知识点_冲冲冲的博客-CSDN博客_java重点算法
集合学习
Map
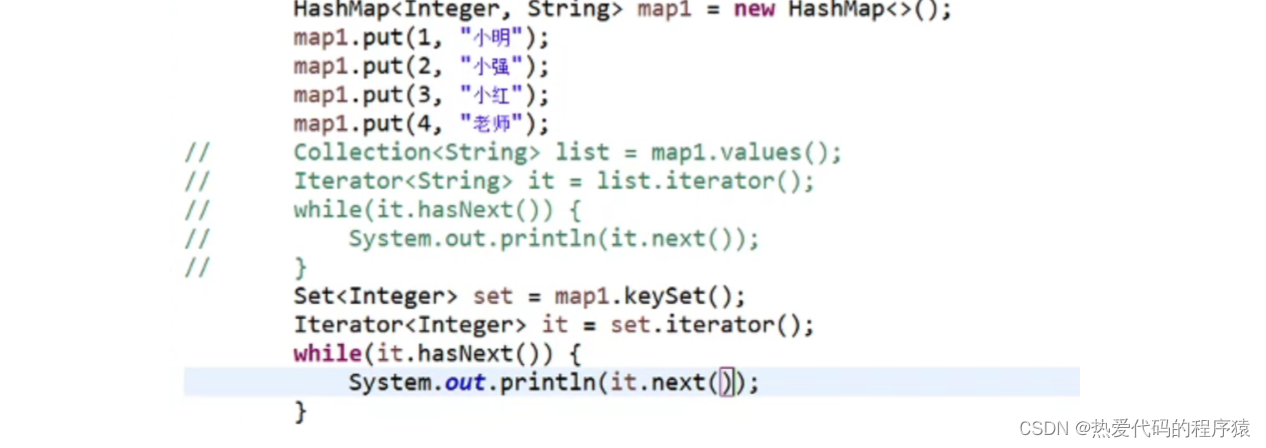
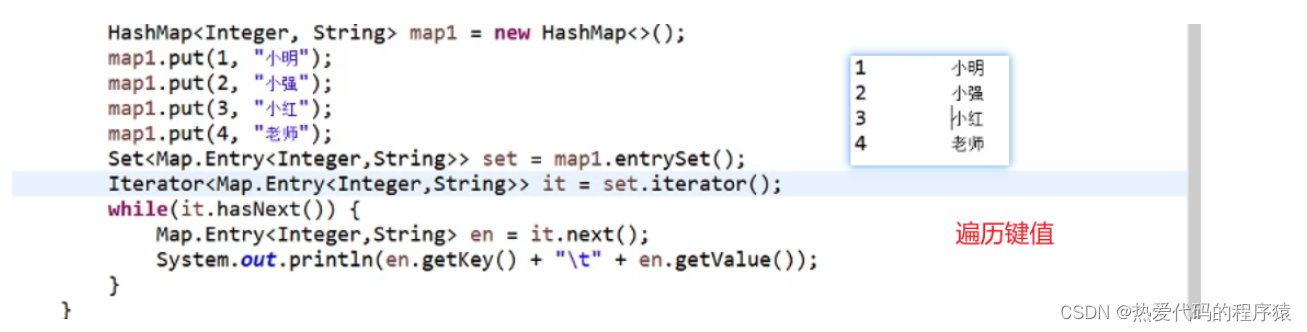
HashMap TreeMap
hashmap遍历

1.随机数
(Math.random() * 11 +10); //产生10~20的随机数
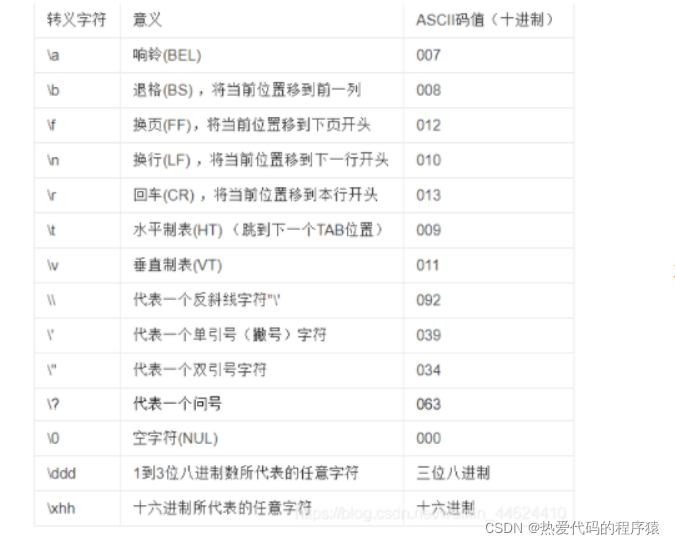
2.转义符
3.substring() 方法截取v字符串
字符串.substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
//beginIndex 起始索引(包括), 索引从 0 开始。endIndex 结束索引(不包括)。
4.判断两个对象是否等价
A.equals(B)
5.随机数控制概率
int d = (int)(Math.random() * 101); //产生100以内的随机数充当概率
if (d <= 75)
(75%的概率干嘛)
else
(25%d 概率干嘛)
6.toCharArray() 获取字符串的每个字符
String Str = "www.runoob.com";
char[] 字符数组 = Str.toCharArray(); //字符串改为字符数组
7.BigInterger操作大数

BigInteger比较大小可以用compareTo方法来比较,小于则返回-1,等于则返回0,大于则返回1
8.Math类的常用方法
Math.sqrt() //计算平方根
Math.cbrt() //计算立方根
Math.hypot(x,y) //计算 (x的平方+y的平方)的平方根
Math.pow(a,b) //计算a的b次方
Math.abs(a) //求绝对值
Math.ceil() //向上取整
Math.floor() //向下取整
9.HashSet不重复集合
Set<String> S = new HashSet<String>(); //构造字符串集合S
//主要方法
S.add() //增加元素
S.clear() //从此 set 中移除所有元素
S.remove() //如果指定元素存在于此 set 中,则将其移除
S.size() //返回此 set 中的元素的数量(set 的容量)
10.长度不固定数组
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
arr.add(3);
11.把ArrayList数组转换成普通数组
int len = arr.size(); //获取集合长度
Integer[] newArr = new Integer[len]; //创建数组
arr.toArray(newArr); //转为数组
12.替换字符串中的片段
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("abcdefghijklmn");
str=str.replace(3, 6, "这里被换了"); //变成了 abc这里被换了ghijklmn
13.替换字符串中的一个字符
String str = new String("abcdefghijklmn");
str=str.replace("a", "这里被换了"); //变成了 这里被换了bcdefghijklmn
14、科学计数法
//科学计数法数字转普通数字
double num1 = 50123.12E25;
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(num1);
System.out.println(bd1.toPlainString());
//普通数字转科学计数法
double num2 = 50123.12;
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal(num2);
System.out.println(bd2.toPlainString()); //法一
System.out.println(String.format("%.6E",num2)); //法二
15、split() 方法根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分字符串
String str = new String("Welcome-to-here");
for (String retval: str.split("-"))
System.out.println(retval);
/*
输出结果为:
Welcome
to
here
*/
16、将数值转化为字符串
String.valueOf(数值)
17、测试运行时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
doSomething(); //测试的代码段
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间
18、compareTo()方法比较字符串
1 、如果两个字符串首字母不同,则该方法返回首字母的asc码的差值
若a=“ab”,b=“b”,则输出-1;
若a=“abcdef”,b="b"则输出-1;
2 、如果首字符相同,则比较下一个字符,直到有不同的为止,返回该不同的字符的asc码差值,如果两个字符串不一样长,可以参与比较的字符又完全一样,则返回两个字符串的长度差值
若a=“ab”,b=“a”,输出1;
若a=“abcdef”,b="a"输出5;
若a=“abcdef”,b="abc"输出3;
若a=“abcdef”,b="ace"输出-1;
19、hasNextInt()判断控制台是否输入数字
if(input.hasNextInt()){
do something;
}
else
System.out.println("请输入正确数字!");
20、char型数字转为int型
char a = '5';
int b = a - '0';
21、Scanner资源关闭
流一旦打开,要记得关闭。所有资源型变量都是三部曲:
打开资源 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
操作数据
关闭资源 sc.close(); // 关闭
资源若没有关闭,会产生内存泄露,运行着运行着,内存越来越少,突然,崩溃××,
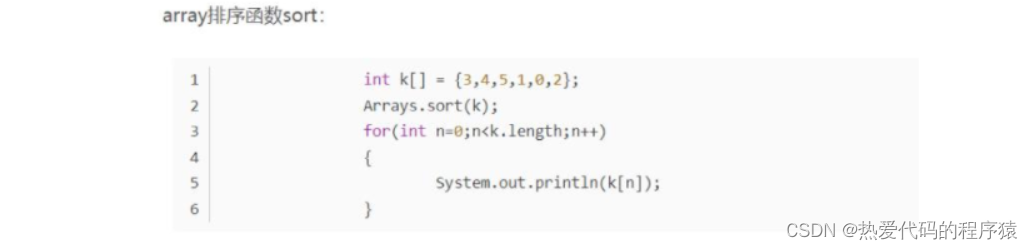
22、array排列数组
23、String与int互相转换
Int----->String(4种方法)
int num=100;
//1
String s1=""+num;
//2
String s2 =String.valueOf(num);
//3
Integer i =new Integer(num);
String s3 =i.toString();
//4
String s4 =Integer.toString(i);
String---->Int (2种)
String s="100";
//1
Integer ii =new Integer(s);
int x=ii.intValue();
//2
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
24、Calendar 的用法
Calendar rightNow = Calendar.getInstance(); // 子类对象
// 获取当前年
int year = rightNow.get(Calendar.YEAR);
// 获取当前月,0~11对应1月到12月
int month = rightNow.get(Calendar.MONTH);
// 获取当前日
int date = rightNow.get(Calendar.DATE);
//获取当前钟点
int hour=rightNow.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
//获取上午下午
int moa=rightNow.get(Calendar.AM_PM);
if(moa==1)
System.out.println("下午");
else
System.out.println("上午");
//当前时间
System.out.println(year + "年" + (month + 1) + "月" + date + "日"+hour+"时");
//set设置时间 add增加时间 get获取操作后的时间
rightNow.set(年 , 月 , 日); //年月日是设置的时间
rightNow.add(Calendar.YEAR,-10); //在设置的时间上减少10年
rightNow.add(Calendar.DATE, -10); //在设置的时间上减少10天
System.out.println(rightNow.getTime());
25、indexOf() 方法
String string = "aaa456ac";
//查找指定字符在字符串中的下标。在则返回所在字符串下标;不在则返回-1.
System.out.println(string.indexOf("b")); // indexOf(String str); 返回结果:-1,"b"不存在
// 从第四个字符位置开始往后继续查找,包含当前位置
System.out.println(string.indexOf("a",3));//indexOf(String str, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
//(与之前的差别:上面的参数是 String 类型,下面的参数是 int 类型)参考数据:a-97,b-98,c-99
// 从头开始查找是否存在指定的字符
System.out.println(string.indexOf(99));//indexOf(int ch);返回结果:7
System.out.println(string.indexOf('c'));//indexOf(int ch);返回结果:7
//从fromIndex查找ch,这个是字符型变量,不是字符串。字符a对应的数字就是97。
System.out.println(string.indexOf(97,3));//indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
System.out.println(string.indexOf('a',3));//indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
//查找指定字符串在字符串中的下标。在则返回所在字符串下标;不在则返回-1.
System.out.println("zhangchen".indexOf("chen"));
}
26、scanner接受char类型字符
char sex=scanner.next().charAt(0);
//charAt()的用法
String str = "abc";
char ch = str.charAt(0);
char ch2 = str.charAt(1);
//这时候ch是a,ch2是b;
27、正则表达式匹配字符串
String s = "zhangchen";
String z = "[^aeiou]+[aeiou]+[^aeiou]+[aeiou]+";//正则表达式
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(z);//模板
Matcher m = p.matcher(s);
System.out.println(m.matches());
28、答案输出为txt文件(简化try/catch)
File file = new File("c:\\1.txt"); //路径是这样的,没有错,运行后会在C盘目录下生成一个1.txt文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
fw.write("123213");//向文件中复制内容
fw.close();
29、进制转换
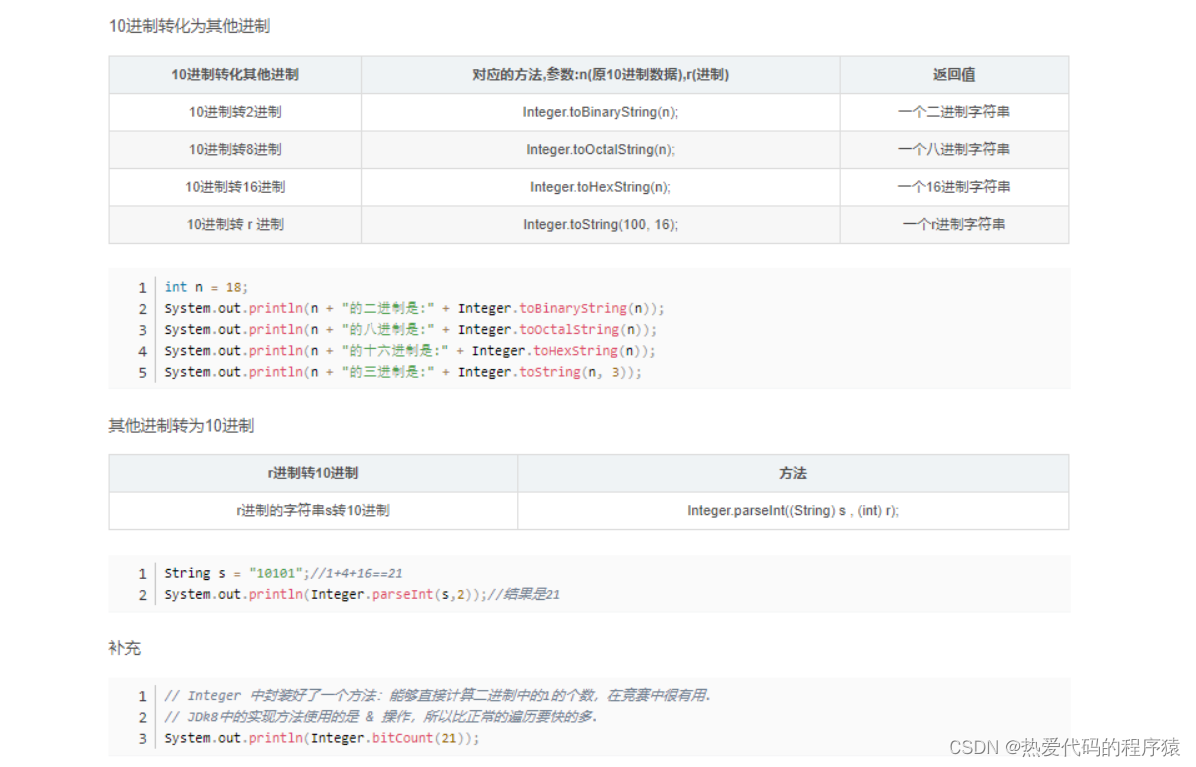
30、java.util.Collections.ncopies()方法
ncopies(int, T) 方法用于返回一个不可变列表组成的n个拷贝的指定对象。
// 参数
// n-- 在返回列表中元素的个数。
// o-- 在返回列表中反复出现的元素
// 返回值
// 方法调用返回的不可变列表组成的n个拷贝的指定对象。
List list = Collections.nCopies(5, "zhang");
// create an iterator
Iterator itr = list.iterator();
System.out.println("Values are :");
while (itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
31、String.join()拼装字符串
// 参数
// 参数一:每个元素要添加的分隔符
// 参数二:需要添加分隔符的字符串
// 返回值
// 拼接后的字符串
String joinString = String.join("-","welcome","to","China");
System.out.println(joinString);
// 输出结果为:
// welcome-to-China
32、String.contains()用法
从后往前遍历查找对应字符串,找到对应字符串结束返回数据,返回值为int类型,返回查找字符串首个字符位置(从0开始查找),未找到返回 -1;
lastIndexOf() 方法有以下四种形式:
int lastIndexOf(char ch)
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
int lastIndexOf(String str)
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
// 参数
// ch -- 字符。
// fromIndex -- 开始搜索的索引位置。
// str -- 要搜索的子字符串。
34、两次回车结束运行
while (true){
//dosomething;
if(in.nextLine().equals("")){
if(!in.nextLine().equals("")){
continue;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
算法方法
1.二分法查找
二分法的解释是: 在一个按照升序排列的数组或集合中,首先判断数组的最中间的元素大于还是小于要查找的值,如果中间的元素大于查找的值,说明想要查找的值在这个数组的前半部分, 反之想要查找的值在这个数组的后半部分, 然后继续取出这个前半部分数组的中间元素 与要查找的值作比较,如此反复下去,直到找到为止。
好处:大大缩减了查找次数,降低性能消耗,进而缩短查找时间。
适用于:升序排列的数组
原理:利用升序和用数组下标,分成区间来查找
package 算法方法最终精简版_带解析;
public class A01_二分法 {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
int count = 0;
while (left < right) {
System.out.println("left"+left);
System.out.println("right"+right);
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
System.out.println("mid"+mid);
if (nums[mid] >= target)
right = mid;
if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
}
// 第一个while循环执行完后 left=4,right=3(下标)
while (left < nums.length && nums[left++] == target){
// nums[left++] 每执行一次,left自加一次
// left < nums.length 保证结果在最后一个的时候 不会超出数组长度,在最后一个检测完后立即退出循环
// 计算有几个相等的数字(执行几次循环 counter+几)
count++;
System.out.println("left<len"+left);
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A01_二分法 demo = new A01_二分法();
int a [] = {5,7,7,8,8,8};
System.out.println(demo.search(a,8));
}
}
package 算法方法最终精简版_带解析;
public class A01_my二分法 {
// 普通方法查找数字(暴力查找)
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// int a[] ={5,7,7,8,8,8};
// int num=8;
// int counter=0;
// for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){
// if(num==a[i]){
// counter++;
// }
// }
// System.out.println(counter);
// }
/*//二分法 直接查找第一个匹配元素
public int binarySearch(int array[],int num){
int count = 0;
System.out.println("****************使用二分法查找****************");
int mid = 0; // 检索的时候
int left = 0; //用left和right两个索引控制它的查询范围
int right = array.length - 1;
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
count++;
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(array.length - 1 == i){
System.out.println("抱歉,没有找到");
}else if (array[mid] < num){
left = mid;
}else if (array[mid] > num){
right = mid;
}else {
System.out.println(array[mid] + "找到了,在数组下标为" + mid + "的地方,查找了" + count + "次。");
break;
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Test demo = new Test();
int array[] = {5,7,7,8,8,10,11};
demo.binarySearch(array,10);
}
*/
// 二分法查找数字
public int search(int []a,int b){
int counter=0; //匹配的次数
int left=0, right=a.length-1;
while(right>left) {//计算出left最小值
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(b>a[mid]) {
left = mid+1;
}else if(b<=a[mid]) {//等于的情况归为前半部分,往前找 直到找到最前面的一个
right = mid;
}
System.out.println(left);
}
// left 3 4 5 left 3 4 5
while(left<a.length && a[left++]==b){//4 5 6
// left 3 4 5 left 4 5 6
// while( a[left++]==b && left<a.length){//4 5 执行两次没有6,因为6不能通过第二个条件
counter++;
// left 4 5 6
System.out.println(left);
System.out.println(left-1);//在下标为此的地方匹配到了
}
return counter;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A01_my二分法 test = new A01_my二分法();
int arr[] ={5,7,7,8,8,8};
System.out.println(test.search(arr, 8));
}
}
2.冒泡排序查找
···待总结



评论区